- Home
- Diagnosis Guide
- Ball Of Foot Pain
Ball Of Foot Pain
Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc(Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed By: FPE Medical Review Board

Ball of foot pain is a common problem with around a quarter of all cases of foot pain affecting the ball of the foot.
Pain in the ball of the foot is often linked to high impact sports involving lots of running and jumping but also affects people who regularly wear tight, narrow shoes, particularly high-heels.
In most cases, ball of foot pain comes on gradually due to overuse or repetitive impact but in some cases it comes on suddenly.
There may be tingling, numbness, stiffness and inflammation alongside pain in the ball of the foot, and in most cases, symptoms get worse with activity and ease with rest.
Here we will look at the most common causes of ball of foot pain, how they present and how to treat them. If you pain is more in the bottom of the foot rather than the ball of the foot, then check out the Foot Arch Pain article.
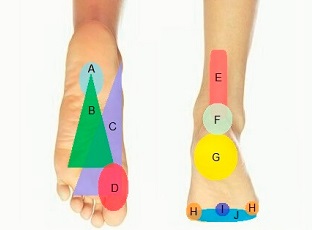
Causes Of Pain In Ball Of Foot
Let’s start by looking at the five most common causes of ball of foot pain and the common features of each, then we’ll go on to look at some of the other possible causes.
1. Metatarsalgia
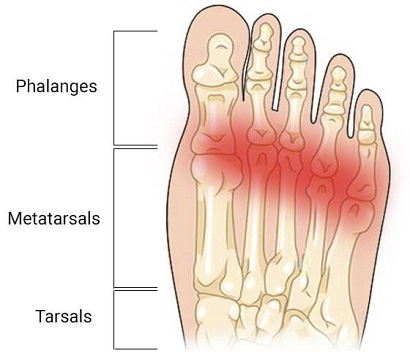
The most common cause of pain in the ball of the foot is metatarsalgia.
Metatarsalgia is an overuse injury that causes inflammation and pain in one or more of the metatarsal bones in the foot.
The metatarsals are the long bones in the forefoot that connect to the toes. Repetitive pressure or overloading through the metatarsal heads leads to irritation and swelling resulting in ball of foot pain.
Common causes of metatarsalgia include high-impact sports involving lots of running and jumping, walking for long periods, wearing high heels or tight fitting footwear, foot deformities and various medical conditions.
Metatarsalgia typically causes a burning or aching pain in the ball of the foot that develops gradually over time rather than suddenly. There may also be associated tingling or numbness in the toes and a shooting pain through the foot, but there isn’t usually any noticeable swelling or lumps. Symptoms tend to extend across the entire ball of the foot, typically get worse with activity and ease with rest.
Metatarsalgia foot pain usually settles down with a combination of rest, ice, orthotics, stretches and strengthening exercises.
You can find out all about how it causes ball of foot pain and the best way to treat it in the Metatarsalgia section.
2. Morton’s Neuroma
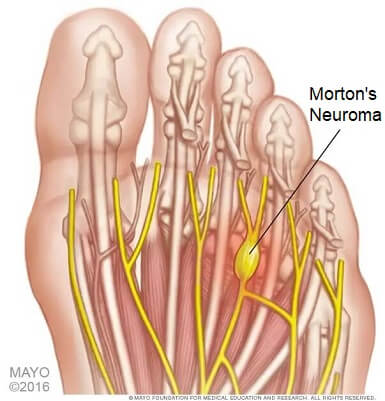
Another common cause of ball of foot pain is a Morton’s Neuroma. One of the classic features of a Morton's neuroma is the feeling that you are standing on a pebble when you walk.
With a Morton’s neuroma there is thickening around one of the nerves in the ball of the foot, usually between the 3rd and 4th toe.
Often, the first symptom of a Morton’s neuroma is tingling and numbness around the nerve which spreads down into the toes. This then progresses to a sharp, stabbing, burning pain in the ball of the foot as the nerve gets more irritated. There may also be a small lump under your foot that you can feel in-between the toes.
Morton’s neuromas are usually caused by wearing tight, narrow or high-heeled shoes, foot deformities e.g. flat feet, sports involving running and jumping and various foot conditions and injuries e.g. arthritis or ligament sprain. They typically affect middle aged people and are much more common in women than men.
Ball of foot pain from a Morton’s neuroma usually improves with a combination of medication, ice, steroid injections, appropriate footwear and orthotics but in some cases, may require surgery.
You can find out all about pain in the ball of the foot from a Morton’s neuroma and how to treat it in the Morton’s Neuroma section.
3. Metatarsal Stress Fractures
Another common cause of pain on the ball of the foot is a metatarsal stress fracture.
Stress fractures are small, subtle fractures, often caused by sudden changes in activity levels e.g. increasing the intensity, frequency or duration of exercise, or changing the surface you work-out on e.g. from a treadmill to roads or soft clay tennis court to a hard court.
Metatarsal stress fractures usually occur when the foot is repetitively overloaded which over time places so much force through one or more of the bones that they break. Metatarsal stress fractures are particularly common during adolescence when the bones are still developing, and in people with osteoporosis. Abnormal foot biomechanics, unsupportive footwear and previous foot injuries also increase the risk of foot stress fractures.
Metatarsal stress fractures usually start off by causing mild ball of foot pain which gradually gets worse and worse. There is often swelling in the ball of the foot and there may be a hard lump over the fracture site. The area is often tender to touch and activities like walking and running become increasingly painful.
If your ball of foot pain is from a stress fracture, then it is really important to rest from any aggravating activities. This may mean using a special walking shoe, splint and/or crutches for a few weeks. Over time, the bone will gradually heal. Regularly applying ice and taking pain-relieving medications and anti-inflammatories will help to reduce the pain in the ball of your foot.
You can find out all about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options for this cause of ball of foot pain in the Foot Stress Fractures section.
4. Sesamoiditis
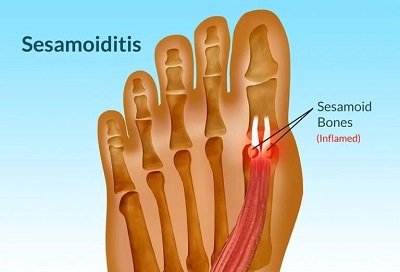
Sesamoiditis can also cause ball of foot pain around the bottom of the big toe.
The sesamoid bones are two small pea-sized bones that sit inside the tendons that run directly underneath the base of the big toe.
Sesamoiditis is characterized by inflammation and pain in the sesamoid bones, which can be caused by overuse, repetitive stress, or injury. Athletes and dancers are particularly susceptible to sesamoiditis due to the high impact and pressure placed on the balls of their feet.
Symptoms of sesamoiditis include tenderness and pain in the ball of the foot, swelling, difficulty bending or straightening the big toe, and difficulty walking or bearing weight on the affected foot.
Treatment for sesamoiditis typically involves rest, icing, and anti-inflammatory medication to reduce ball of foot pain and inflammation. Taping, padding or orthotics may also be used to provide support and relieve pressure on the affected area. In severe cases, immobilization with a cast or walking boot may be necessary to allow the sesamoid bones time to heal properly.
The best way to prevent pain in the ball of the foot from sesamoiditis is to avoid high-impact activities or gradually increase their intensity over time, wear properly fitting, flat shoes with adequate support and cushioning, and maintain good foot flexibility with stretching exercises.
You can find out all about sesamoid ball of foot pain including the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options in the sesamoiditis section.
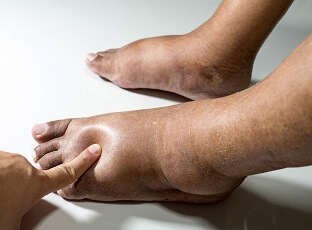
5. Foot Bunions
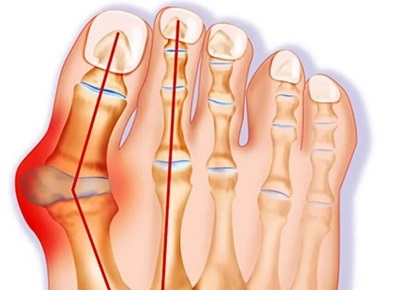
Bunions are a common foot condition that can cause pain in the ball of the foot, especially in the area near the big toe.
A bunion is a bony bump that develops on the joint at the base of the big toe, which can push the big toe inwards towards the other toes and cause the ball of the foot to become wider.
The pressure and friction caused by bunions can result in ball of foot pain, as well as other symptoms such as redness, swelling, stiffness and difficulty moving the big toe. The exact cause of foot bunions is unknown but it is thought that a variety of factors including genetics, arthritis, and wearing shoes that are too tight or don't provide proper support increase the risk. Bunions are a progressive condition and early intervention is essential to prevent the condition from worsening.
Treatment for bunions may include wearing properly fitted shoes with a wider toe box, using orthotics or other devices to relieve pressure on the affected area and correct the toe position, strengthening and stretching exercises, and taking over-the-counter pain medication to reduce ball of foot pain. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the bunion and realign the affected joint.
You can find out loads more about pain in the ball of the foot from bunions including the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and best treatment and prevention options in the Foot Bunions section.
Other Causes Of Ball Of Foot Pain
There are a number of other less common causes of ball of foot pain:
- Hammer, Mallet or Claw Toe: toe deformities where the toes become bent or curled in different positions, causing the ball of the foot to bear too much weight, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Hallux Rigidus: wear and tear leads to stiffness and pain in the big toe which can affect activities such as walking.
- Sprain: Overstretching and/or tearing of one of the ligaments of the foot, can lead to pain in the ball of the foot and other parts of the foot. This can happen due to sudden twisting or stretching of the foot, causing damage to the ligaments.
- Arthritis: Various types of arthritis, most notable osteoarthritis and gout, can cause inflammation and pain in the ball of the foot, particularly in the joint at the base of the big toe. This can cause stiffness, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected joint.
- Corns & Calluses: These are areas of thickened skin that can develop on the ball of the foot, as well as elsewhere, due to pressure and friction. Corns are small, cone-shaped bumps that may be hard or soft, while calluses are rough patches of skin that can be quite large.
- Plantar Warts: aka verruca vulgaris. A skin infection causes small, rough lumps to develop on the skin, often containing tiny black dots. They are particularly common on weight-bearing areas of the foot
- Lisfranc Fracture: a type of foot fracture that affects the bones and ligaments in the middle of the foot, causing swelling and pain in the ball of the foot. Lisfranc injuries usually occur from a fall or sudden trauma to the foot rather than gradually from overuse
- Freiberg’s Disease: a condition that affects the metatarsal bones, causing stiffness and ball of the foot pain. Freiberg’s disease occurs when the blood supply to the metatarsal bones is interrupted, causing damage to the bone tissue
- Altered Foot Biomechanics: People with high or low foot arches may experience pain in the ball of the foot due to excessive pressure and weight bearing through the area. Altered foot biomechanics can also cause the foot to be less flexible, leading to pain and discomfort when walking or standing and can also result in knee pain
- Improper Footwear: Wearing shoes that are too tight, too loose, or have high heels places much more pressure, weight and friction through ball of the foot which can lead to pain
- Obesity: Carrying excess weight puts extra pressure on the ball of the foot, leading to pain and discomfort. This can make it difficult to walk or stand for long periods of time.
Ball Of Foot Pain Treatment
Treatment for pain in the ball of the foot will depend on the underlying cause but will usually involve a combination of:
- Rest: to allow the affected structures in the ball of the foot time to heal
- Regular Ice: applying an ice pack for 10-15 minutes every couple of hours helps to reduce ball of foot pain and inflammation
- Orthotics: specially designed inserts for your shoes can help to cushion, protect or take weight off the ball of the foot and thus reduce pain
- Exercises: stretching and strengthening exercises help to improve the flexibility, strength and control around the foot which helps to take pressure of the structures around the ball of the foot
- Comfortable Footwear: one of the best things you can do to reduce ball of foot pain is to switch to wearing flat, wide, cushioned shoes that provide good support. Ditch those high heels and narrow, pointy shoes!
You can find out more about specific treatment for the different causes of ball of foot pain in the following articles:
- Metatarsalgia Treatment
- Morton’s Neuroma Treatment
- Bunion Treatment
- Foot Stress Fracture Treatment
- Hammer/Mallet/Claw Toe Treatment
- Foot Corns & Callus Treatment
- Gout Toe Treatment & Prevention
- Hallux Rigidus Treatment
- Sesamoiditis Treatment
- Plantar Wart Treatment
Ball Of Foot Pain Summary
Pain in the ball of the foot is a common problem that can affect people at any age.
There five most common causes of ball of foot pain are Morton’s neuroma, metatarsalgia, metatarsal stress fractures, sesamoiditis and bunions.
Other possible causes include toe deformities, hallux rigidus (stiff big toe), arthritis, plantar warts, ligament sprain, corns/calluses, altered foot biomechanics and Freiberg’s disease.
Ball of foot pain typically affects people who play high-impact sports that involve lots of running and/or jumping or wear tight-fitting or high-heeled shoes.
Treatment for pain in the ball of the foot usually involves a combination of rest, ice, orthotics, exercises, steroid injections, medication and wearing appropriate footwear. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
You may also be interested in the following articles:
- Pain On Top Of Foot
- Toe Joint Pain
- Pain On Outside Of Foot
- Inner Foot Pain
- Bottom Of Foot Pain
- Foot Lumps
- Bump On Bottom Of Foot
Related Articles
References
- Foot pain and foot health in an educated population of adults: results from the Glasgow Caledonian University Alumni Foot Health Survey. Journal Of Foot & Ankle Research. August 2018
- Pain In The Ball Of The Foot. NHS. March 22
- Metatarsalgia. Cleveland Clinic. February 2019
Page Last Updated: 20th November, 2024
Next Review Due: 20th November, 2026