- Home
- Common Foot Problems
- Tendonitis Guide
- Anterior Tibialis Tendonitis
Tibialis Anterior Tendonitis
Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc(Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed By: FPE Medical Review Board

Tibialis anterior tendonitis is a common condition that causes pain and discomfort in the front of the ankle and foot.
Also known as anterior tibial tendonitis or anterior tibialis tendonitis, it is caused by inflammation of the tibialis anterior tendon, which runs along the front of the lower leg and attaches to the foot.
Tibialis anterior tendonitis can affect people of all ages, but usually affects people who are active or participate in high-impact activities such as running, jumping, or dancing that place stress on the foot. It typically affects people over the age of 40 due to reduced tendon elasticity and blood flow.
Here, we will explore what tibialis anterior tendonitis is and look at the common causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options as well as prevention techniques and the recovery process.
What is Tibialis Anterior Tendonitis?
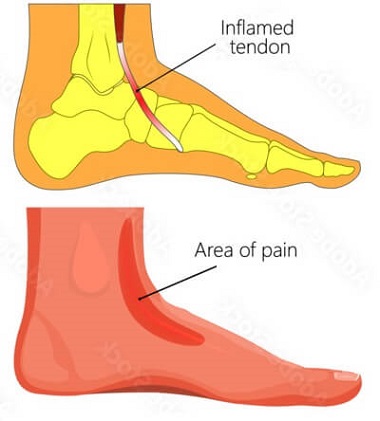
Tibialis anterior tendonitis is an overuse injury that causes foot pain and inflammation in the tendon at the front of the ankle.
The tendon connects the tibialis anterior muscle, located on the front of the shin, to two of the bones in the top of the foot, the first metatarsal and the medial cuneiform.
The tibialis anterior muscle is responsible for dorsiflexion, or pulling the foot upwards towards the shin, and helps turn the foot inwards.
When the tibialis anterior muscle is overused or misused, it can cause damage to the tendon and result in anterior tibial tendonitis, making it difficult to walk, run, or participate in physical activity.
Causes Of Tibialis Anterior Tendonitis
The most common cause of tibialis anterior tendonitis is overuse, usually from repetitive or prolonged activities that cause strain and stress on the tibialis anterior tendon. This overuse can lead to inflammation, micro-tearing, and degeneration of the tendon.
Common causes of anterior tibial tendonitis include:
- Sports Activities: Sports that involve repetitive movements, such as running, jumping, and dancing, can put excessive strain on the tibialis anterior tendon, leading to tendonitis
- Footwear: Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate support or are too tight can cause undue stress on the tendon
- Anatomical Abnormalities: People who have flat feet, high arches, or other structural problems that affect the alignment of their feet and legs may be more prone to developing anterior tibialis tendonitis
- Training Errors: Sudden changes in training intensity or frequency, or inadequate warm-up or cool-down routines, can increase the risk of developing anterior tibial tendonitis
- Aging: As we age, our tendons lose some of their elasticity, making them more prone to injuries, particularly tendonitis
- Muscle Imbalance: weakness and tightness in the calf and foot muscles place excess stress through the tendon making it prone to inflammation and tearing
Additionally, people who have suffered from previous ankle injuries or who are overweight may be at a higher risk for developing tibialis anterior tendonitis.
How Common is Anterior Tibial Tendonitis?
Tibialis anterior tendonitis is a relatively common condition, particularly in individuals who participate in activities that require repetitive ankle and foot movements. This includes runners, dancers, and other athletes.
It is estimated that around 10% of runners will experience anterior tibial tendonitis at some point during their running career.
However, it can also affect individuals who are not particularly active especially if they have experienced previous ankle injuries. Tibialis anterior tendonitis is a common cause of top of foot pain, particularly near the ankle.
Symptoms Of Tibialis Anterior Tendonitis
Common symptoms of tibialis anterior tendonitis include:
- Foot Pain: and tenderness on the front of your ankle and shin and along the top of the foot. Typically an aching or throbbing pain that worsens with activity
- Swelling: or inflammation in and around the tendon
- Ankle Stiffness: there may be limited range of motion in your ankle or foot
- Activity Limitations: difficulty walking, running, or participating in physical activity
- Weakness: difficulty lifting your foot off the ground and instability in your ankle
Anterior tibialis tendonitis pain may be felt during or after exercise and can range from mild to severe. Symptoms typically worsen with activity and improve with rest.
In some cases, a popping sound may be heard or felt in the ankle at the time of injury. If this is accompanied by immediate swelling then it is likely that the tibialis anterior tendon has completely ruptured.
Diagnosing Anterior Tibial Tendonitis
If you are experiencing symptoms of tibialis anterior tendonitis, it's important to seek an accurate diagnosis from a healthcare professional.
In most cases, a physical therapist or doctor can diagnose tibialis anterior tendonitis by performing a physical exam and reviewing your medical history. Diagnostic tests, such as X-rays or an MRI, may also be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Physical Exam

To accurately diagnose tibialis anterior tendonitis your healthcare provider will begin with a physical examination to assess your symptoms and determine the severity of your condition.
During the examination, they may ask you about your medical history, previous injuries, and any other conditions that may be contributing to your symptoms.
They will look for signs of inflammation and tenderness along the front of the ankle. They will then get you to perform certain movements to assess the strength and range of motion in the ankle and foot.
Imaging Tests
In some cases, they may recommend imaging tests to confirm the diagnosis of tibialis anterior tendonitis and rule out other potential conditions or injuries. Imaging tests may include:
- X-rays: to rule out any bone fractures or other abnormalities in the affected area.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): to obtain detailed images of the soft tissues in the affected area, such as tendons, muscles, and ligaments, to help diagnose anterior tibial tendonitis.
- Electromyography (EMG): to evaluate the electrical activity in your muscles and nerves and help determine if there is any damage
Differential Diagnosis
Tibialis anterior tendonitis can sometimes be mistaken for other foot injuries or conditions, however, there are some key differences that can help distinguish them:
- Stress Fractures: small breaks in one or more of the foot bones which are typically caused by repetitive impact or trauma to a bone, rather than the overuse or repetitive strain on the tendon with anterior tibialis tendonitis
- Shin Splints: typically cause pain along the inner part of the shin, whereas tibialis anterior tendonitis causes pain on the front of the shin.
- Plantar Fasciitis: While both conditions can cause difficulty walking or participating in physical activity, plantar fasciitis typically causes pain in the heel or arch of the foot, whereas anterior tibialis tendonitis causes pain on the front of the ankle and shin.
Ankle tendonitis is a common problem and can affect any of the foot and ankle tendons. Other common types of foot tendonitis include:
- Achilles Tendonitis: at the back of the ankle
- Peroneal Tendonitis: on the outer side of the ankle
- Posterior Tibial Tendonitis: on the inner side of the ankle
- Extensor Tendonitis: on the top of the foot
Once you have received a diagnosis of tibialis anterior tendonitis, your healthcare provider will recommend a treatment plan based on the severity of your condition. Treatment options can range from conservative, non-invasive therapies to more aggressive surgical interventions.
Treatment For Tibialis Anterior Tendonitis
Tibialis anterior treatment aims to reduce pain and inflammation, correct any foot deformities and restore normal walking pattern so you can return to your usual activities without any discomfort or stiffness.
In most cases, anterior tibial tendonitis can be treated conservatively, i.e. without the need for surgery, unless there are significant tears in the tendon.
#CommissionEarned from Amazon on qualifying purchases
Non-Surgical Treatments
Conservative treatment for tibialis anterior tendonitis aims to alleviate pain and inflammation while promoting healing and may include:
- Rest: One of the most important things you can do for anterior tibial tendonitis is to rest the affected foot and protect it from further damage. Avoid activities that cause pain or aggravate the injury to allow the tendon time to heal and consider using crutches or a brace to keep weight off the foot. If you need to stay active, try low-impact activities that won’t exacerbate your symptoms, like swimming or cycling
- Regular Ice: Applying ice to the affected area for 20-30 minutes several times a day can help reduce tibialis anterior pain and inflammation. Be sure to wrap the ice pack in a towel or cloth to avoid skin damage
- Compression: Wearing a compression bandage such as tubigrip can help to reduce and swelling in the foot and ankle. Tubigrip should be worn double thickness during the day, but should not be worn overnight
- Elevation: Keeping your foot elevated can also help reduce the swelling and pain associated with anterior tibial tendonitis. Prop your foot up on a pillow or cushion, or use a special leg elevation cushion to keep it elevated above your heart level for best results
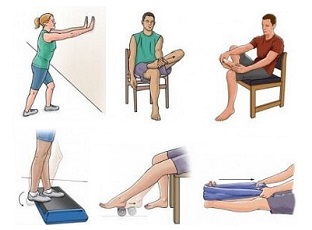
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help to improve strength and flexibility in the ankle. They will give you a customized treatment plan to help you recover from tibialis anterior tendonitis which may include rehab exercises, electrotherapy, acupuncture and friction massage
- Medication: Over-the-counter NSAIDs e.g. ibuprofen or naproxen, and pain relievers e.g. paracetamol can help to reduce tibialis anterior pain and inflammation
- Immobilization: In some cases, immobilization may be necessary to allow the affected area time to rest and heal properly. Your healthcare provider may recommend a cast or walking boot to limit movement and prevent further injury
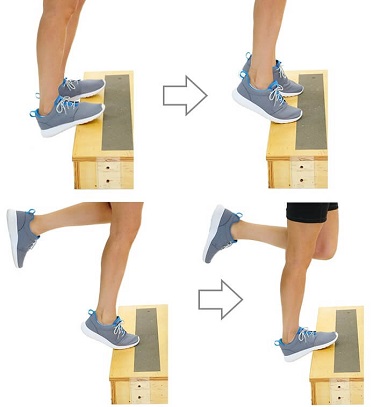
- Exercises: Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises are a vital part of rehab with anterior tibialis tendonitis. It is really important to regain full strength, stability and flexibility in the foot to prevent the tendonitis from returning and to reduce the risk of future ankle injuries.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Corticosteroid injections can really help to reduce localised inflammation and pain in the tendon but should only be carried out by a qualified healthcare professional. They can temporarily weaken the tendon so it is important to rest for a few days
Home Remedies
There are a number of things you can do at home as well to help treat anterior tibialis tendonitis:
- Proper Footwear: Wearing supportive shoes with good arch support can help prevent further damage to the tibialis anterior tendon. Look for shoes with a wide toe box and good cushioning.
- Maintain A Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put extra strain on the tibialis anterior tendon. Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk of future injuries and promote healing
- Topical Creams: Over-the-counter creams like Arnica or Tiger Balm can provide excellent pain relief and reduce inflammation when applied topically to the affected area - many people swear by them
- Supplements: Natural supplements like turmeric or omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce tibialis anterior pain and swelling. However, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider before taking any supplements as they are not suitable for everyone
Surgical Options
Your doctor may recommend surgery for tibialis anterior tendonitis if conservative treatments and immobilization do not provide relief or your condition is severe. Surgical options for tibialis anterior tendonitis may include:
- Tendon Repair: Where the damaged portion of the tendon is repaired with sutures and if necessary reattached to the bone
- Tendon Transfer: If the tendon has torn completely, the remaining parts may not be long enough to be sewn back together. Tendon transfer surgery involves moving a healthy tendon from another part of the body to replace the damaged tibialis anterior tendon.
- Debridement: Debridement surgery involves removing damaged tissue from the affected area to promote healing.
Surgical intervention is usually only necessary if the tendon has completely ruptured. It is typically considered a last resort for treating tibialis anterior tendonitis and is only recommended if all other treatment options have failed.
How To Prevent Anterior Tibialis Tendonitis
Tibialis anterior tendonitis can be a painful condition to deal with, but by taking proper preventative measures, you can greatly reduce the risk, such as:
- Wear properly fitted shoes with good arch support to avoid overpronation. Avoid wearing high heels for extended periods of time, as they can put a lot of stress on your feet and ankles
- Replace shoes that have worn out soles, as they can cause unnecessary strain on your feet and legs
- Use orthotics or inserts in your shoes if needed, to help improve foot alignment and provide extra support
- Gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercise, rather than jumping into an intense workout routine all at once
- Avoiding repetitive motions that can stress the tibialis anterior tendon such as jumping and kicking
- Take breaks and rest when you feel pain or discomfort
- Maintain a healthy weight to avoid putting extra stress through the tendon
- Stretching exercises can help improve the flexibility of the muscles and tendons in your feet and ankle, reducing the risk of injury
- Strengthening exercises for your feet and ankles can help improve stability and balance, reducing the risk of overuse injuries like tibialis anterior tendonitis
- Balance exercises can also help improve ankle stability, reducing the risk of ankle sprains and other injuries.
By following these preventative measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing tibialis anterior tendonitis.
Recovery Time For Tibialis Anterior Tendonitis
Recovering from anterior tibial tendonitis takes time and patience and the length of recovery depends on factors such as the severity of your tendonitis, your age, and your overall health. In general, following your doctor's instructions and taking good care of your foot can help speed up the recovery process and prevent future injuries.
Be patient and allow your body the time it needs to heal fully, and you can expect to return to your normal activities soon. If you try and do too much too soon, you will keep aggravating the tendon. It needs time for the inflammation to settle and for the tendon to heal.
While recovery time can vary, most people with tibialis anterior tendonitis can expect to recover fully within 4-12 weeks with proper care. If you require surgery, it can 6 months to a year to make a full recovery.
Anterior Tibialis Tendonitis Summary
Tibialis anterior tendonitis is a common foot injury that occurs when the tibialis anterior tendon becomes inflamed.
Common causes of anterior tibialis tendonitis include overuse, improper footwear, sudden increases in activity level, and trauma to the foot or ankle.
Common symptoms of tibialis anterior tendonitis include top of foot pain, swelling, and tenderness along the front of the ankle and foot, particularly during activity.
Treatment for tibialis anterior pain includes conservative measures such as rest, ice, compression, elevation, medications and strengthening and stretching exercises as well as physical therapy, orthotics, and immobilization in severe cases. Surgery is rarely necessary unless the tendon has ruptured.
The best ways to reduce the risk of developing tibialis anterior tendonitis is to wear appropriate footwear, gradually increase activity levels, and avoid sudden increases in intensity or duration of exercise.
You may also been interested in the following articles:
- Foot Pain Diagnosis
- Pain On Top Of Foot
- Pain On Side Of Foot
- Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
- Foot Lumps & Bumps
- Foot Pain From Running
- Foot Numbness
Page Last Updated: 02/28/24
Next Review Due: 02/28/26