- Home
- Diagnosis Guide
- Foot Lumps
- Lump Side Of Foot
Lump On Side Of Foot
Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc(Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed By: FPE Medical Review Board
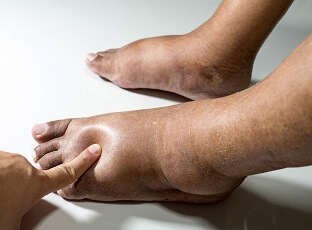
A lump on the side of the foot is a common problem and can be quite worrying, but in most cases, it’s nothing serious.
There are lots of different things that can cause lumps and bumps on the side of the foot.
There may be a problem with one of the foot bones, a build-up of fluid, inflammation from over-use or a benign growth.
It is very uncommon for a foot lump to be cancerous but any new growth should always be evaluated by your doctor.
Here we are going to look at the different causes of a lump on the side of the foot and how to identify which one you have. We will then go on to look at the best ways to treat them. If you are more bothered by pain than swelling, check out the Outer Foot Pain and Inner Foot Pain articles.
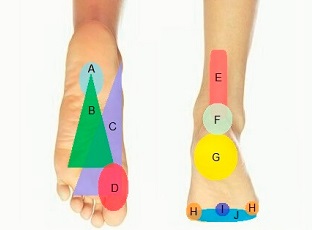
What Causes a Side Of Foot Lump?
A lump on the side of the foot may be caused by:
- Bone Damage: a hard lump on the side of the foot may indicate a problem with one of the foot bones e.g. fracture, bunion, cuboid syndrome, accessory navicular or a bone spur
- Excess Fluid: a build-up of fluid can collect and form a soft side of foot lump e.g. ganglion cyst, papules or sebaceous cyst
- Benign Growth: a non-cancerous growth of tissues may form firm nodules under the skin e.g. plantar fibroma
- Medical Conditions: certain medical conditions can result in a lump on the side of the foot e.g. gout or arthritis
- Overuse: repetitive overuse of the foot can result in swelling and a soft bump on the side of the foot e.g. tendonitis
Each of these causes of a side of foot lump will present slightly differently and require different treatment. So let’s start by looking at the eight most common causes of lumps on the side of the foot and then we’ll go on to look at the more unusual ones.
1. Bunions
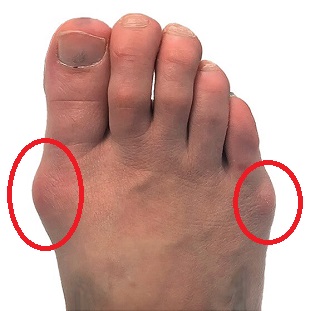
The most common cause of a hard lump on the side of the foot is a bunion. Bunions can occur at the:
- Big Toe: most common site for bunions, aka Hallux Valgus. Causes a lump on big toe
- Little Toe: less common, aka bunionette or Tailor’s Bunion. Causes lump by little toe
With a hallux valgus, the big toe shifts out of position, slowly deviating towards the second toe. As the tip of the toe moves inwards, the base of the big toe shifts outwards causing a hard bump on the side of the foot. If you have a lump on your big toe, chances are it’s a bunion!
With a Tailor’s Bunion, the tip of the little toe shifts inwards towards the fourth toe and the base of the little toe shifts outwards, resulting in a hard lump on the outside of the foot. If you have a lump by your little toe, it’s most likely a bunionette!
Over time, as the toe shifts over further, the side of foot lump becomes more prominent and may start to rub on your shoe.
Common foot bunion symptoms include:
- Redness: and inflammation over the bunion from friction on footwear
- Hard Lump: on side of foot
- Toe Deviation: the toe gradually shifts further over and may end up crossing over the top of the neighbouring toe
- Pain: tends to get worse the further the toe deviates
- Stiffness: in the affected toe
Bunions are typically caused by wearing tight, narrow shoes, particularly if they have a high heel. There is also thought to be a genetic link so if someone in your family has bunions, you are more likely to develop one.
The sooner you start treating a bunion lump on the side of the foot, the better as the deviation gets harder to correct the greater it is.
You can find out more about this common cause of side of foot lumps and how to treat them in the Foot Bunions section.
2. Foot Cysts
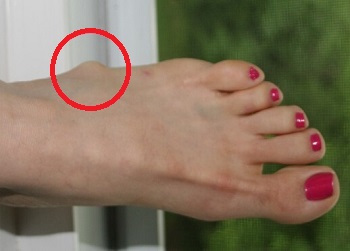
Another common cause of a lump on the side of the foot is a ganglion cyst.
Ganglion cysts are small, fluid-filled pockets that form just below the skin. They can occur anywhere in the foot but are most common on the side or top of the foot. If they develop on one of the toes, they are know as a digital mucous cyst.
What causes ganglion cysts to form is unknown but they are thought to be linked to repetitive micro-injuries (from friction or pressure) and arthritis. Ganglia are three times more common in women than men and are most common between the ages of 20-50.
A ganglion lump on the side of the foot is usually round or oval and can vary in size. Typically they are fairly small (pea-sized) but they can grow much larger. Ganglion foot lumps are usually soft but firm to touch rather than hard.
A lump on the side of the foot from a ganglion cyst is not normally painful unless it starts to rub on your shoes or press on one of the surrounding nerves which can cause some tingling in your foot.
Painless ganglion lumps on the foot don’t need to be treated and may go away on their own over time. However, if the ganglion becomes painful or affects foot movement or daily activities such as walking, then treatment such as medication, splinting, aspiration or occasionally surgery may be recommended.
You can find out more about foot cysts and their causes, symptoms and treatment in the ganglion cysts and digital mucous cysts sections.
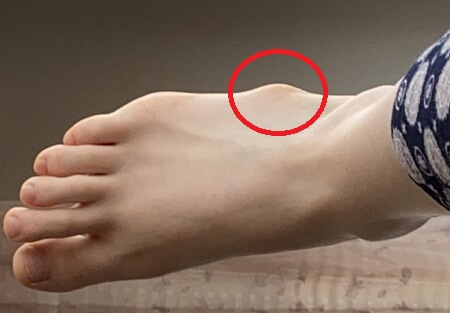
3. Foot Tendonitis
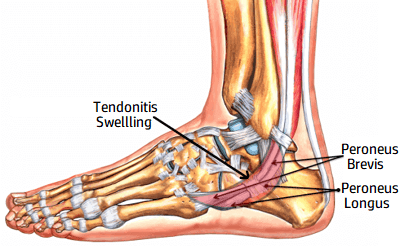
A bump on the side of the foot may be due to tendonitis – inflammation of one of the foot tendons. There tends to be more of a general swelling than a specific lump with tendonitis.
Tendonitis usually develops due to repetitive overuse, altered foot biomechanics, or an injury e.g. ankle sprain.
In the early stages of foot tendonitis, there is typically a sharp or burning pain where the tendon attaches to the foot bone, which is worse during activity. Over time, you may notice a soft bump on the side of the foot where the tendon has started to thicken.
Common types of tendonitis that can cause a lump on the side of the foot are:
- Peroneal Tendonitis: bump on outside of foot towards the ankle
- Posterior Tibial Tendonitis: bump on inside of the foot near the medial foot arch
There are lots of treatment options for foot tendonitis including ice, exercises and orthotics. You can find out more about how to treat a tendonitis bump on the side of the foot in the Foot Tendonitis section.
4. Fractures
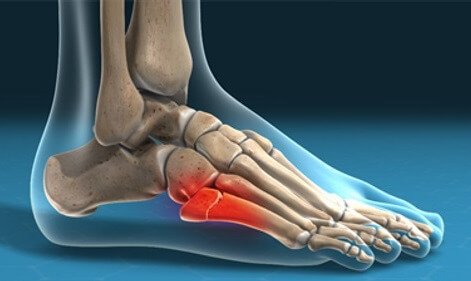
Another possible cause of a painful lump on the side of the foot is a fifth metatarsal fracture, a break in the long bone on the outer side of the foot.
The most common fractures to cause side foot bumps are:
- Jones Fracture: break in the 5th metatarsal. Typically caused by repetitive overuse or a sudden force through the outer side of the foot where the foot gets twisted away from the body. Particularly common in athletes and dancers. Results in a painful hard lump on side of foot.
- Stress Fracture: tiny cracks in one or more of the foot bones. Typically caused by overuse e.g. repetitive jumping or long distance running, or suddenly increasing activity levels. Pain gradually gets worse over time and there may be a tender bump on side of foot over the fracture site
- Avulsion Fracture: a small piece of bone is pulled of the tuberosity at the proximal end of the fifth metatarsal. Usually caused by sudden forced twisting of the foot causing immediate pain and difficulty walking. Aka Pseudo Jones fractures, they are the most common type of fifth metatarsal fracture.
- Dancers Fracture: a diagonal break in the middle of the bone, the metatarsal shaft, usually due to twisting injuries or with awkward landing.
Treatment for foot fractures will vary depending on the type, severity and location of the fracture but will usually include a combination of PRICE (protect, rest, ice, compression & elevation), medication and exercises. Surgery is only needed if there is significant pain, deformity or displacement of the bone.
You can find out more about the common causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention options in the Fifth Metatarsal Fracture section.
5. Plantar Fibroma
A lump in the arch of the foot may be due to a plantar fibroma. A plantar fibroma is a benign (non-cancerous) growth where one or more nodules form around the plantar fascia.
Plantar fibromas are usually small (less than 1 inch) forming a firm bump in the arch of the foot. They may form in isolation or in clusters.
Plantar fibromas are twice as common in men as women and are thought to be linked to genetics. They are usually only painful when there is direct pressure through the fibroma foot lump.
There are a number of different options with treatment for plantar fibromas including injections, exercises, orthotics and surgery.
Plantar fibromas are the most common cause of a lump in the arch of the foot and you can find out more about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options in the plantar fibromatosis section.
6. Gout Foot
Another common cause of a lump on the big toe that is painful, red and swollen is foot gout. Gout is caused by a build-up of uric acid crystals that collect in the big toe joint. Symptoms usually develop rapidly, often at night and can lead to intense pain in the big toe.
Uric acid is a natural product produced by the body when it breaks down certain chemicals, but problems arise when the kidneys aren’t able to filter it out quick enough. This leads to the formation of hard, spiky crystals in joints. Gout can affect any joint in the body but most commonly affects the big toe.
Recurrent bouts of gout are common without correct treatment and, over time, can lead to the formation of tophi - large, visible lumps of urate crystals that develop under the skin.
You can find out more about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options in the Gout Foot section, as well as how to reduce the risk of recurrent episodes.
7. Piezogenic Papules
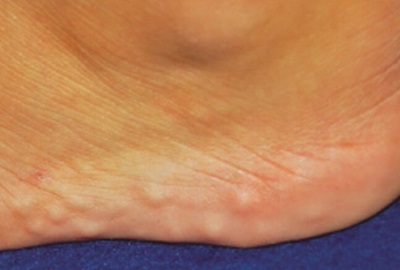
A common cause of small lumps on the side of the foot is piezogenic papules.
Around 60% of the population will develop these lumps at some point in their lives.
These clusters of small lumps around the heel are typically visible when you are standing or bearing weight through your heels, and usually disappear when you take the weight off your foot.
Piezogenic lumps on the side of the foot are usually around 0.2cm in diameter, and may be groups of up to 20 lumps.
Weakness in the connective tissue results in pockets forming just underneath the skin. When you stand, the pressure pushes fatty tissue into these pockets forming small lumps which may or may not be painful.
You can find out all about these small lumps on the side of the foot in the piezogenic papules section.
8. Accessory Naviculars
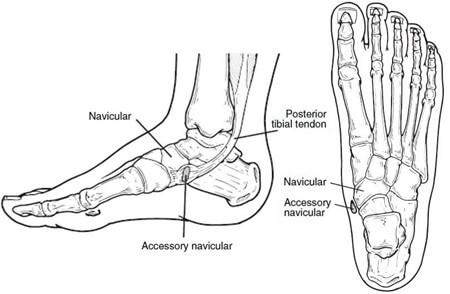
A hard lump inside the arch of the foot may be caused by an accessory navicular.
An accessory navicular is a congenital abnormality (meaning its present from birth) where there is an extra piece of bone or cartilage found in the medial foot arch.
The medical terms for an accessory navicular are an os navicularum or os tibiale externum.
In most cases, an accessory navicular goes completely unnoticed, not causing any symptoms. However, following an injury (e.g. ankle sprain), or chronic irritation (from repetitive friction or excessive activity) an accessory navicular can result in:
- Bony Prominence: hard lump on side of foot in the medial foot arch
- Redness & Swelling: around the foot lump
- Pain: and a throbbing sensation in the arch of the foot, particularly during activity
Asymptomatic cases of accessory naviculars don’t require any treatment. If however, the accessory lump on the side of your foot becomes painful, it can be treated with a combination of immobilization, ice, medication, physical therapy and orthotics. In severe cases, the accessory navicular may need to be surgically removed, however this is rare.
You can find out loads more about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment in the accessory navicular syndrome section.
9. Corns/Calluses
Skin lumps on the side of the foot are usually caused by corns or calluses.
- Corns: small, pale, yellow circular areas of hard, raised skin. May caused some discomfort
- Calluses: larger areas of thickened, hardened skin. Usually painless
Corns and calluses typically develop in response to repetitive friction or pressure on the skin e.g. from ill-fitting footwear.
There are lots of different treatment options for corn and callus lumps on the side of the foot including creams, chemicals, pumice stones and medications.
You can find out lots more about the causes, diagnosis and best treatment options in the Foot Corns & Calluses section.
Rare Causes Of A Side Of Foot Bump
There are a few other less common causes of lumps on the side of the foot:
- Bursitis: inflammation of one of the small fluid-filled sacs that sit between soft tissues and bone to reduce friction – most common is heel bursitis
- Cuboid Syndrome: dislocation of the cuboid bone which may cause a small hard lump at the side of the foot. If you have ongoing pain on the outer side of your foot after an ankle sprain, there’s a high chance it’s cuboid syndrome
- Lipoma: soft, fatty lumps that grow under the skin – more commonly found on top of foot but can occur on the side of the foot
- Sebaceous Cysts: small lumps caused by blocked glands or hair follicles
- Bone Spur: more commonly found around the heel, occasionally you can get a bone spur on the side of the foot which forms a hard lump
- Rheumatoid Nodules: if you have rheumatoid arthritis, there is a high chance the lump on the side of your foot is due to a build-up of inflammatory particles and fibrin which form firm nodules
- Tumor: most lumps on the side of the foot are benign (non-cancerous) but any new lumps should be checked by your doctor, particularly if they are large, fast growing, irregularly shaped and increasingly painful
Lumps and bumps can occur anywhere on the foot and you might be interested in the following articles:
- Lump On Top Of Foot
- Bump On Bottom Of Foot
- Lump On Heels
- Lump On Toes
- Swollen Feet
- Swollen Foot Treatment
Lump On Side Of Foot Summary
There are lots of possible causes of foot lumps.
A lump on the side of the foot near your toes is most likely due to bunions, foot gout, digital mucous cyst or corns/calluses.
A lump on the outside of the foot may be caused by peroneal tendonitis, jones fracture, ganglion cyst, avulsion fracture, fifth metatarsal fracture or cuboid syndrome.
A lump on the inside of the foot or in the medial arch may be caused by posterior tibial tendonitis, piezogenic papules, plantar fibroma or accessory navicular.
A lump on the side of the foot near the heel may be caused by heel bursitis, piezogenic papules or bone spur.
Lumps that can occur anywhere on the side of the foot may be caused by ganglion cysts, stress fractures, bursitis, bone spurs, lipoma, sebaceous cysts, rheumatoid nodules or cancer.
Treatment will depend on what is causing the lump on the side of your foot and you can find out more about the best treatment options by using the links above.
You may also be interested in the following articles:
- Pain On Top Of Foot
- Inner Foot Pain
- Outer Foot Pain
- Pain In Ball Of Foot
- Pain On Bottom Of Foot
- Foot Swelling Causes
- Morning Foot Pain
Related Articles
Page Last Updated: 19th November, 2024
Next Review Due: 19th November, 2026